
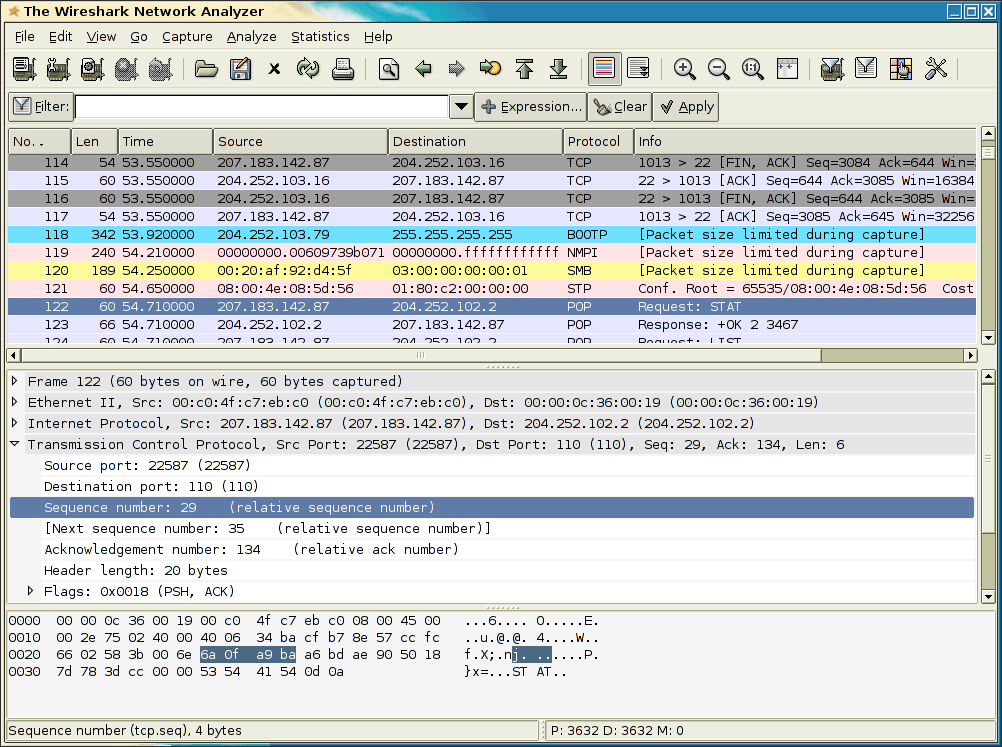
In the Arguments field, enter your command line flags for tshark.exe.įor this tutorial, we specify the following parameters to capture raw output from a specific device to a set of revolving data files (but none of these parameters are uniquely required to run TShark as a service): If you installed Wireshark in the default location, this is
Wireshark windows 2008 full#
In the Application field, enter the full path to the TShark executable, tshark.exe.

Select Application > Add to open the Add Application window:
Please make a note of where you installed it as we will need that location in a later step.
Wireshark windows 2008 install#
To configure TShark to run as a service with AlwaysUp:ĭownload and install AlwaysUp, if necessary.ĭownload and install Wireshark, if necessary. TShark is a command line component designed to capture network traffic. You might be surprised how much traffic seemingly simple operations can generate.Wireshark is a popular set of network protocol analyzer tools Play around with these statistics screens after performing some typical operations on your own network. Then, stroll over to the top bandwidth users and politely ask them to stop using your corporate file servers to back up their MP3 collections! To save yourself some NSLOOKUP queries, make sure that your Wireshark capture options include the “Enable network name resolution” flag so that you can see hostnames in place of IP addresses when viewing the conversations traffic report. The “Bytes A -> B” and “Bytes A<-B” headings show bandwidth usage by direction. You can click the “Bytes” column heading to sort the report so that the largest bandwidth conversations appear at the top. You can then take information like that and use it for capacity planning, network performance optimization, baselining, and troubleshooting.Īnother item on the Statistics menu is “Conversations.” The dialog box comes up by default to the Ethernet tab, but if you’re interested in where network traffic is being generated on your LAN, click the IPv4 tab and view the byte traffic by conversations between IP addresses. With appropriate capture filters, this kind of information can help you see firsthand the network impact of user actions such as opening a share, copying a file over the network, opening an intranet or Internet page, and so forth. The resulting dialog box gives you relevant capture details in the top half and some useful performance details in the bottom half, such as the average packet size, average number of packets per second, and average bytes per second (or Mbits if you prefer). First, start a capture so that you have some data to work on, then stop it and choose Statistics > Summary. There are a couple of techniques that are handy for this sort of thing, and they’re both on the Wireshark “Statistics” menu.

(For example, I was a little surprised to see on my own network that the simple act of navigating to a subfolder on a network share generated about 2000 SMB packets.) You might want to test certain procedures and user actions to learn which are more “expensive” in terms of bandwidth. You might be interested to see which computers seem to be creating more traffic than others. One of the most useful things you can do with a packet sniffer like Wireshark is gain an understanding of who and what is responsible for the lion’s share of communications traffic on your network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
